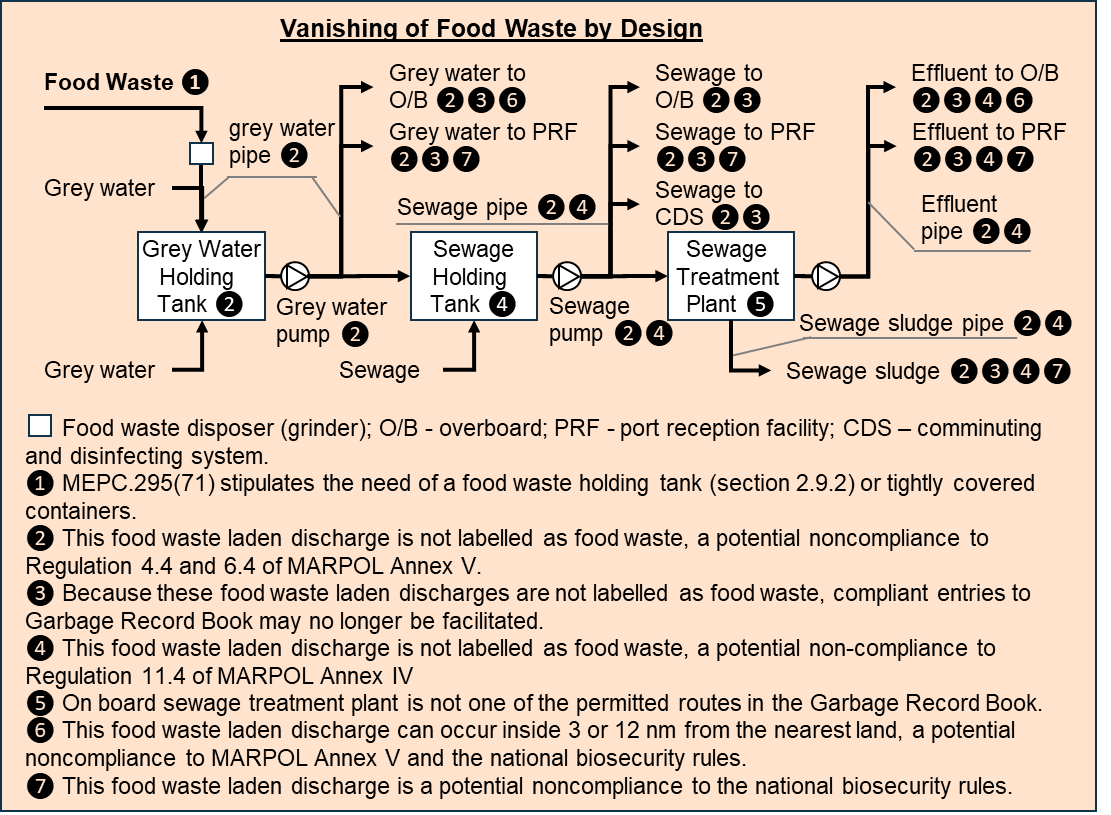
This is part 2 of our short series on the ongoing discussion on conditioning water. Please click here to read part 1.
Sewage treatment plants (STPs) are tested and approved using an influent of 500 mg/l TSS. The concentration of ship’s vacuum sewage . It needs to be conditioned (or reduced) using freshwater or greywater to allow STPs to deliver their treatment performances proven during the tests. Currently, not many ships, except a few dozen cruise ships trading in Alaska, concern about STP discharge performances, because the regulations have not asked them to. But this will change when the IMO’s sewage rules are now being revised to confirm the lifetime performance of the STPs (see our four-part series on the revision of MARPOL Annex IV). Environmental rules need to be effective and practicable. Approving STPs at 500 mg/l TSS and using them at 2,000 mg/l is neither effective nor practicable. Conditioning water was introduced under this revision work in 2020 (PPR 8/7) so that its usage can be compliant, consistent, and prevented from abuse.
Conditioning water aims to reduce concentrations of vacuum sewage for compliant operation of STPs in accordance with their approved conditions. However, dilution also aims to reduce concentrations, but it aims to pollute in disguise. Tell them apart on paper and in practice is crucial.
The IMO tried to restrict dilution machines by tightening their performance standards by applying the dilution compensation factor, Qi/Qe, or influent flow over effluent flow, of less than 1 (MEPC 227(64), 2012). The intention is good, but the outcome is ineffective. Because there are no requirements to monitor and record real-time Qi/Qe factor to ensure compliance over the lifetime performance of these dilution machines. Flow meters, taken for granted in land-based wastewater industry, are perceived as burdensome for ships. Without flow meters, dilution machines can use far more dilution water than its approved conditions without anyone knowing.
IMO’s MEPC subcommittee PPR (Pollution Prevention and Response) tries to tell the difference between conditioning and dilution by their definitions. Dilution is defined as dilution water introduced after the STP influent sample point to reduce concentrations. Conditioning water is defined as freshwater introduced to reduce the concentrated sewage to the test conditions of, say, 500 mg/l TSS (PPR 10/12). These definitions are helpful for type tests but less so during STP operation because there are no regulatory requirements to mount influent sample points to dilution machines approved with Qi/Qe < 1. Also, to analyse influent TSS concentrations as a way of verifying genuine use of conditioning water can be burdensome if at all practicable.
A dilution ban was proposed in 2018 (PPR 6/14) by removing Qi/Qe <1. An allowance of up to 5% of Qe was introduced for essential STP services such as cleaning, polymer make-up, etc. The initiative could simplify implementations, enhance effectiveness, and reduce burdens. After all, dilution should not be the solution to pollution. However, dilution machines were proposed to be reinstated in 2021 (PPR 9/14), and again, with no requirements to monitor or record real-time Qi/Qe to confirm the lifetime performance. Making compromises while maintaining the effectiveness and practicality of the rules requires knowledge and skill. The revision work is ongoing.
HAMANN AG STPs do not use dilution (Qi/Qe = 1). HAMANN AG recommends the use of grey water to condition concentrated vacuum sewage on board because this provides added environmental credentials, and it is there already – so no reason to use precious fresh water. To size the STPs correctly to accommodate grey water is important, and we will discuss this in a separate article. We proactively engage with regulatory development and do our best to help our customers with compliant and future-proofing solutions.